H.T. Kurkjian, M.D.
The Prostate
Hosted by OKdrs.com
_____________________________________________________________________________________
Dr. Kurkjian fast facts and demography
[Kurkjian Home][Kurkjian FAQ][Kurkjian Services]
_____________________________________________________________________________________
THE PROSTATE
 |
Prostate cancer kills more than 30,000 people a year
in the United States. However, with early diagnose it is possible to be cured from cancer
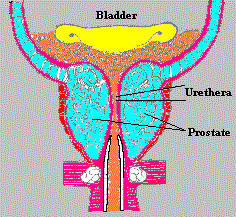
of the prostate and have a normal life. Prostate Anatomy The prostate is a walnut sized gland that plays a role in sexual function. It is located in the lower region of the human body between the bladder and the urethra, a channel which passes through the prostate and drains the urinary bladder. |
Benign Hyperplasia of the Prostate
Beginning at age 40, the prostate, under the influence of male hormones, starts to enlarge. As it gets bigger, it will squeeze the urethra that passes through it, causing problems with urination. These problems consist mostly of frequency (frequent urination), hesitancy (difficulty in starting and voiding), nocturia (getting up at night to pass urine), and sometimes urinary retention (not being able to void).The pressure that builds up in the bladder with incomplete emptying can cause urinary infections. Back -pressure into the kidneys may result in failure of the kidneys.
Prostatitis
This is another category of prostate disease and is usually caused from inflammation of the prostate. The symptoms are lower back pain, pain in the perineum and pain in the lower part of the body.
Cancer Of the Prostate
A more serious disease is cancer of the prostate. it starts in the prostate and gradually grows from the prostate on out. It may spread by blood or lymph into the bones and if not treated, may lead to death.
Diagnosis is made most commonly by digital examination of the prostate. If a nodule or an area of increased firmness in the prostate is felt, then the following tests are usually performed:
- Biopsy - Obtaining a sample with a needle for laboratory examination.
- Cystoscopy - Inspecting the bladder and the prostate with a special instrument.
- Ultrasound - Imaging with sound waves.
- I.V.P. - X-rays of the kidney and the bladder.
If the biopsy is positive for cancer, then further studies are done to make sure the cancer is contained in the prostate. These studies are:
- Bone Scan - A nuclear study of the bones whereby a mild radioactive chemical is injected into a vein and the bones are scanned.
- Chest x-ray -
- Prostate Specific Antigen - A blood test to check on the amount of prostate tissue in the blood. Normal range is less than 4 ng/mL in males.
- Acid Phosphatase - A blood test to check if the cancer is localized.
- Computerized Axial Tomography of the Pelvis - This is also known as a CATScan, a special x-ray to check on the enlarged lymph nodes or extension of the tumor outside the prostate. This test is optional.
If these are negative, then most probably the cancer is contained.
Treatment
Radical Prostatecomy - This procedure is
accomplished by completely removing the prostate and removing some of the pelvic lymph
nodes. Some of the complications of prostatectomy are:
- Sexual dysfunction - This happens only in 5% of the patients who undergo surgery for benign prostatic enlargement. However, after radical surgery for cancer, even with the newer nerve sparing techniques, sexual dysfunction is a common problem.
- Leakage of urine. This is a very rare after surgery for benign disease, but not uncommon after prostatectomy for cancer.
Medical Treatment
Alpha-Blockers are medications that relax the
prostate and make urination easier. An important side effect is lower blood pressure.
In conclusion, it is important to have the prostate examined and a PSA done at least once a year in most men after the age of 40. In men which have had a prostate operation for non-malignant disease, or who are fifty years or older, a digital exam and a PSA every six months is indicated.
Disclaimer: Although OKdrs.com undertakes reasonable efforts to keep the information contained herein accurate, Okdrs.com does not warrant the accuracy, completeness, timeliness or merchantability or fitness for a particular purpose of the information contained herein nor in any way endorse the individuals described herein . In no event shall Okdrs.com be liable to you or anyone else for any decision made or action taken by you in reliance on such information. The above warranties are the only warranties of any kind either expressed or implied including warranties of merchantability or fitness for any particular purpose.