Epididymitis
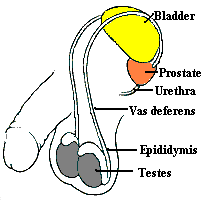 |
Epididymitis is a condition
whereby the epididymis is inflamed. This structure is a fingerlike
organ that is attached to the testicle in a C-like fashion. On its
bottom part this organ is attached to the vas. The function of this
organ is to help in the maturation of the human sperm.
Etiology:
The cause of this problem is usually unknown. However
it is more common in patients with a urethral stricture, urethritis (inflammation), increased abdominal pressure as in pushing or lifting
heavy objects and sometimes vasectomy.
|
Signs and symptoms:
Pain in the scrotum sometimes radiating to the lower part of
the abdomen. Fever, chills, nausea and lack of appetite are other common
symptoms.
Physical exam:
This reveals tender and swollen epididymis.
Lab:
Urine culture may sometimes be positive. Ultrasound may show
cyst formation.
Treatment:
Antibiotics, heat, elevation of the testicles and rest will
usually be very helpful. It is to be noted that acute epididymitis will take at
least two weeks to resolve. If this condition becomes recurrent and chronic,
after several bouts, Epididymectomy may be considered. This is surgical removal
of the epididymis, done usually at a hospital or outpatient surgery. The removal
of the epididymis results in permanent sterility on that side. Recovery from
this procedure usually takes two weeks.